PLYWOOD
PLYWOOD
WHAT IS PLYWOOD
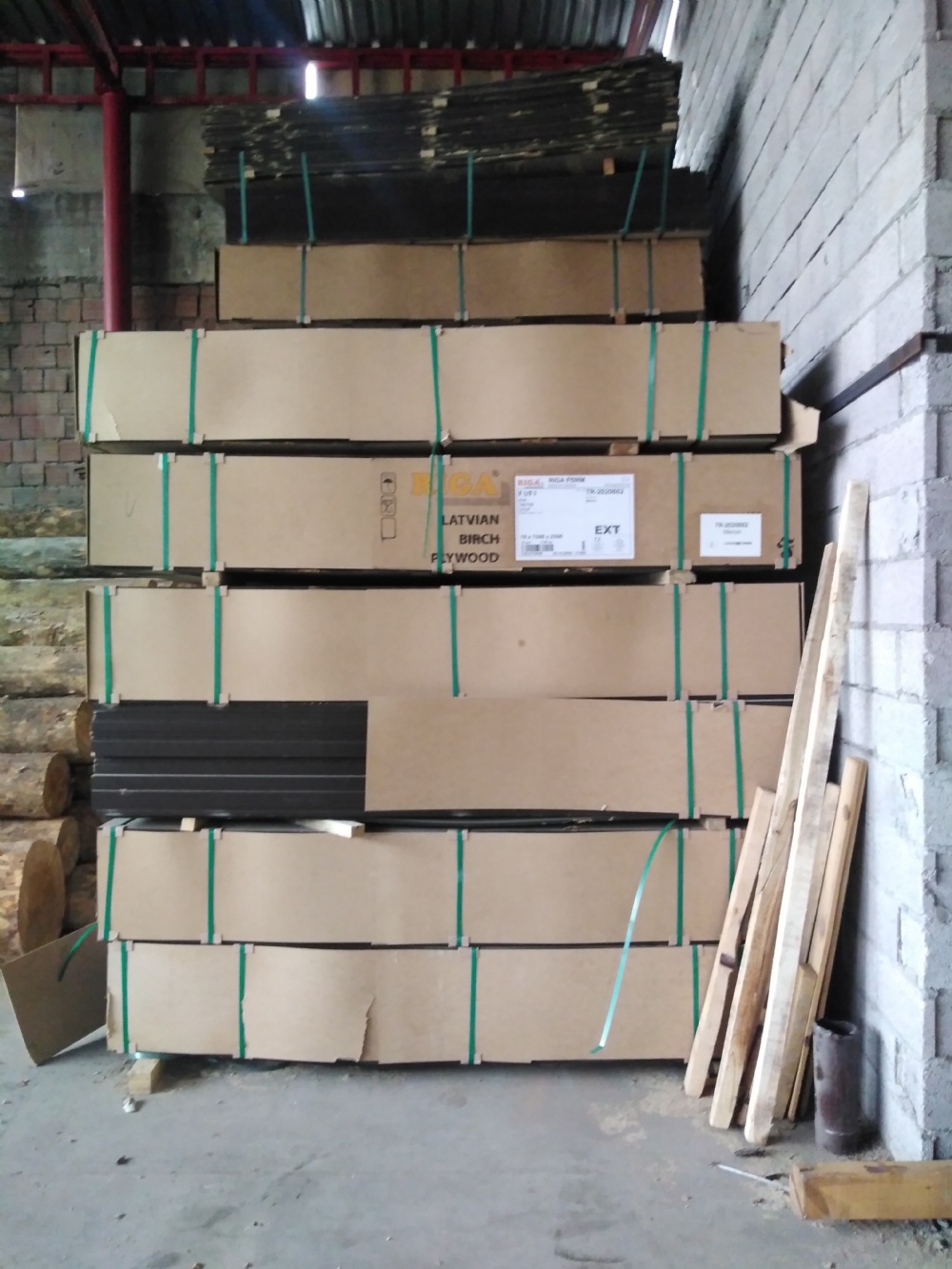
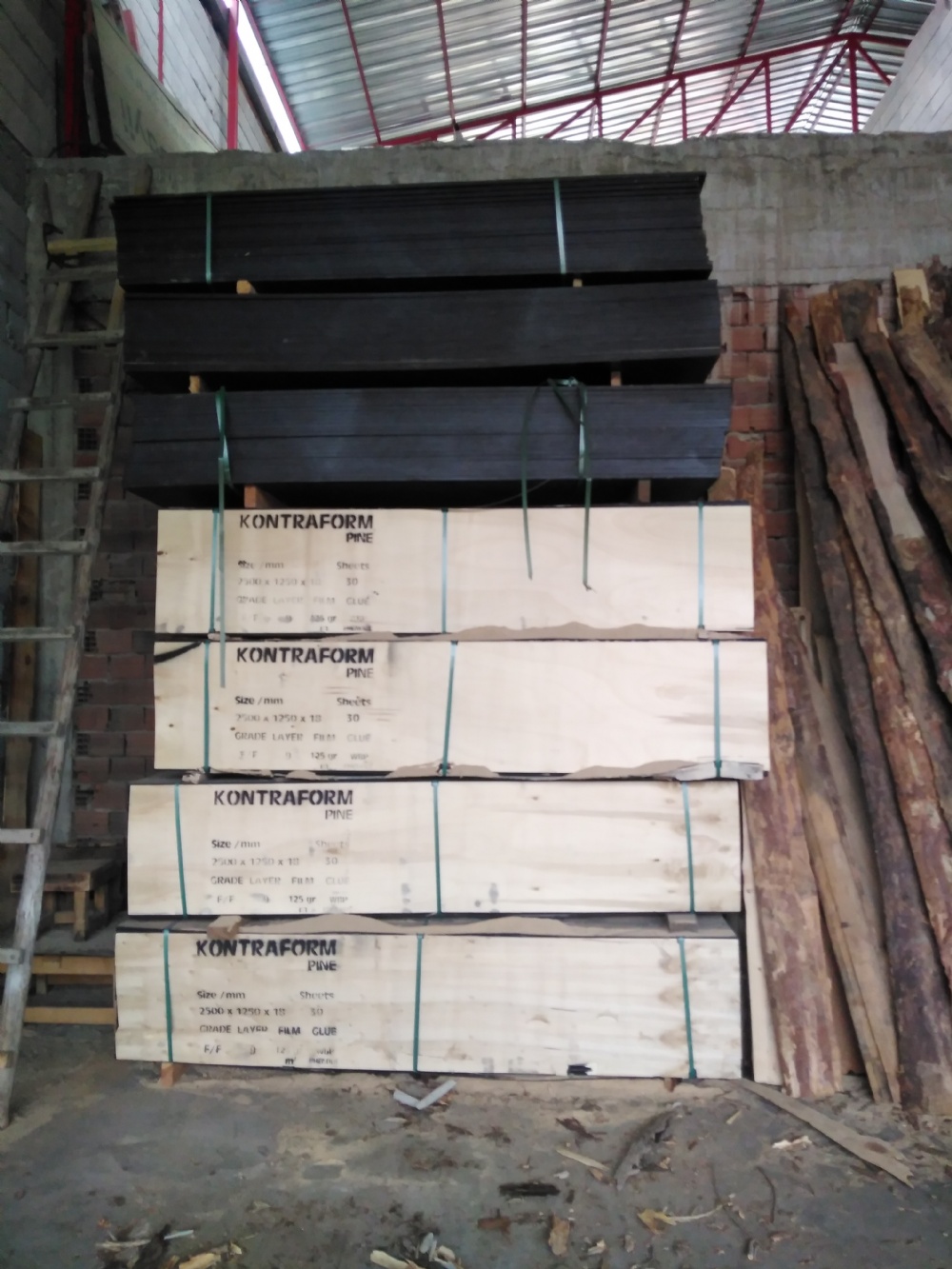
Plywood is a forest product used intensively in the construction sector. Its water resistance and high strength are important for this sector. It is especially used in the preparation of concrete molds. It is a very suitable material for unplastered mold systems, also called gross molds. Plywoods, which are increasingly used today, have replaced traditional wooden molds to obtain gross concrete. As you know, Plywoods are divided into two as filmed and unfilmed.
Contrary to popular belief, the difference between them is not related to durability and only affects the concrete surface. It is correct to use filmed materials on surfaces that will not be plastered and allows you to obtain glossy gross concrete. On surfaces to be plastered, unfilmed plywoods should be used. The concrete surface obtained in unfilmed materials is still gross but not glossy. Thanks to this feature, it allows plastering.
Plywood Classes
BB/BB BB/CP BB/C CP/CP CP/C C
Plywood is different from MDF, high density fiberboard (HDF), block and particleboards. Others are cheap materials and their durability cannot be compared to Birch Plywood varieties.
Areas of Use
IN CONSTRUCTION WORKS
In formwork
In scaffolding platforms
Interior partition and roof covering works
In the floor and parquet industry
ADVANTAGES
It is light.
Since the wood fibers forming the layers are combined in different directions (90 degrees to each other), it is a durable material. It does not break easily.
It can be produced in desired dimensions with a thickness of 6-30 mm.
Its use is widespread in many sectors.
It is resistant to cracking.
It has a high screw holding feature.
It can be easily processed and is environmentally friendly.
It is economical.
The plywood surface can be polished. It can be painted.
It is highly resistant to water.
It is an environmentally friendly product.